1797. 设计一个验证系统
大约 3 分钟
1797. 设计一个验证系统
题目描述
你需要设计一个包含验证码的验证系统。每一次验证中,用户会收到一个新的验证码,这个验证码在 currentTime 时刻之后 timeToLive 秒过期。如果验证码被更新了,那么它会在 currentTime (可能与之前的 currentTime 不同)时刻延长 timeToLive 秒。
请你实现 AuthenticationManager 类:
AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive)构造AuthenticationManager并设置timeToLive参数。generate(string tokenId, int currentTime)给定tokenId,在当前时间currentTime生成一个新的验证码。renew(string tokenId, int currentTime)将给定tokenId且 未过期 的验证码在currentTime时刻更新。如果给定tokenId对应的验证码不存在或已过期,请你忽略该操作,不会有任何更新操作发生。countUnexpiredTokens(int currentTime)请返回在给定currentTime时刻,未过期 的验证码数目。
如果一个验证码在时刻 t 过期,且另一个操作恰好在时刻 t 发生(renew 或者 countUnexpiredTokens 操作),过期事件 优先于 其他操作。
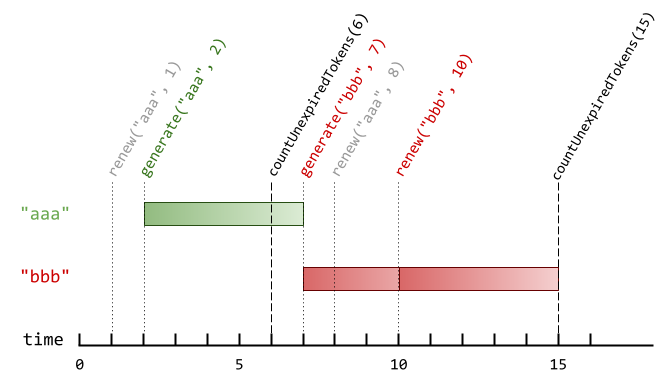
示例 1:
输入:
["AuthenticationManager", "renew", "generate", "countUnexpiredTokens", "generate", "renew", "renew", "countUnexpiredTokens"]
[[5], ["aaa", 1], ["aaa", 2], [6], ["bbb", 7], ["aaa", 8], ["bbb", 10], [15]]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, null, null, null, 0]
解释:
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = new AuthenticationManager(5); // 构造 AuthenticationManager ,设置 timeToLive = 5 秒。
authenticationManager.renew("aaa", 1); // 时刻 1 时,没有验证码的 tokenId 为 "aaa" ,没有验证码被更新。
authenticationManager.generate("aaa", 2); // 时刻 2 时,生成一个 tokenId 为 "aaa" 的新验证码。
authenticationManager.countUnexpiredTokens(6); // 时刻 6 时,只有 tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码未过期,所以返回 1 。
authenticationManager.generate("bbb", 7); // 时刻 7 时,生成一个 tokenId 为 "bbb" 的新验证码。
authenticationManager.renew("aaa", 8); // tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码在时刻 7 过期,且 8 >= 7 ,所以时刻 8 的renew 操作被忽略,没有验证码被更新。
authenticationManager.renew("bbb", 10); // tokenId 为 "bbb" 的验证码在时刻 10 没有过期,所以 renew 操作会执行,该 token 将在时刻 15 过期。
authenticationManager.countUnexpiredTokens(15); // tokenId 为 "bbb" 的验证码在时刻 15 过期,tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码在时刻 7 过期,所有验证码均已过期,所以返回 0 。
提示:
1 <= timeToLive <= 1081 <= currentTime <= 1081 <= tokenId.length <= 5tokenId只包含小写英文字母。- 所有
generate函数的调用都会包含独一无二的tokenId值。 - 所有函数调用中,
currentTime的值 严格递增 。 - 所有函数的调用次数总共不超过
2000次。
思路
时间复杂的分析
根据题目中的提示,所有的函数调用次数总数不超过2000次,那么最大的时间复杂的应该在4*106左右
解题思路
这个题目是设计一个系统,偏向业务的代码,同时时间复杂的要求也不高,我们可以根据题目所表达的意思直接进行模拟,通过某些数据结构进行数据存储,在查询数量时实时计算即可。
数据结构选择
因为涉及数据的更新操作,这边优先选择Map对数据进行存储,每次在更新操作和获取有效数量时进行判断之前的数据是否过期,由于current_time是严格递增的,我们可以把过去的数据删除,减小下一次的计算数量。
如果对时间复杂的有要求,我们可以使用LinkedHashMap或者TreeMap对数据进行存储,然后在获取未过期的数量时是常数的时间复杂度,插入和更新时是lgN的复杂度。
题解
class AuthenticationManager {
Map<String,Integer> map;
int liveTime=0;
public AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive) {
map=new HashMap<>();
liveTime=timeToLive;
}
public void generate(String tokenId, int currentTime) {
map.put(tokenId,currentTime);
}
public void renew(String tokenId, int currentTime) {
if(map.containsKey(tokenId)){
int before=map.get(tokenId);
if(currentTime-before<liveTime){
map.put(tokenId,currentTime);
}
else{
map.remove(tokenId);
}
}
}
public int countUnexpiredTokens(int currentTime) {
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> it=map.entrySet().iterator();
int res=0;
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry=it.next();
int before=entry.getValue();
if(currentTime-before>=liveTime){
it.remove();
}
else{
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
/**
* Your AuthenticationManager object will be instantiated and called as such:
* AuthenticationManager obj = new AuthenticationManager(timeToLive);
* obj.generate(tokenId,currentTime);
* obj.renew(tokenId,currentTime);
* int param_3 = obj.countUnexpiredTokens(currentTime);
*/
